
C# Variables
Introduction to the C# variables
A variable is a name given to a storage area that is used to store values of various data types. Each variable in C# needs to have a specific type, which determines the size and layout of the variable’s memory.
To perform any operation on variables it is essential to define a variable with a particular data type to specify the type of data that the variable can hold in our application. Let’s see a few basic things about variables:
- Variables are nothing but a name given to data value.
- Variables can hold the value of particular data types, for example, int, string, float and so on.
- Declaration and initialization of variables are in separate statements.
- Variables can be defined by multiple separated by a comma and also in single and multi-line till the end of the semicolon.
- Values must be assigned to a variable before we make use of it; otherwise, it will show a compile-time error.
- The value of a variable can be changed at any time until the program accessibility.
Programs process data. Typically, They work as follows:
- First, get data from user inputs, files, or third-party API.
- Second, process the data.
- Third, output the result to the screen or save it to data storage such as a file or database.
The basic value types provided in C# can be categorized as:
| Type | Example |
|---|---|
Decimal types | decimal |
Boolean types | true or false values, as assigned |
Integral types | int, char, byte, short, long |
Floating point types | float and double |
Nullable types | Nullable data types |
C# also allows defining other value types of variable such as enum and reference types of variables such as class, which we will cover in subsequent chapters.
How to Declare Variables in C#?
There are some rules to declare C# Variables:
- We must define a variable name with the combination of numbers, alphabets and underscore.
- Every variable name should start with alphabets or underscore.
- There should not be any white space allowed in between the variable name.
- Variable names should not contain any reserve keywords like int, char, float and so on.
Before using a variable, you need to declare it using the following syntax:
[Data Type] [Variable Name];
[Data Type] [Variable Name] = Value;
[Access Specifier] [Data Type] [Variable Name] = Value;In this syntax:
- [Data Type] - It’s a type of data the variable can hold, such as integer, string, decimal, etc.
- [Variable Name] - It’s the name of the variable to hold the values in our application.
- [Value] - Assigning a required value to the variable.
- [Access Specifier] - It is used to define access permissions for the variable.
They are some suitable methods to describe the variable names in c# programming language:
int num;
float value;
char _name;You can also initialize a variable at the time of definition as follows:
int value = 500;The following table illustrates the most commonly used built-in types:
| Type | Meaning | Examples |
|---|---|---|
int | Integers | 1, 2, 3 |
float | Single-precision floating-point numbers | 1.1F |
double | Double-precision floating-point numbers | 2.5 |
string | Text strings | “Hi” |
char | Characters | ‘a’, ‘b’,’c’ |
bool | boolean values | true, false |
How to Initialize Variables in C#?
To assign a value to a variable called initialization, variables can be initialized with an equal sign by the constant expression, variables can also be initialized at their declaration.
Syntax:
[data_type] [variable_name] = value;
Or
variable_name = value;For example:
int v1=15, v2= 17;
double pi= 3.1416;
char name='dani';
C# Declare multiple variables
To declare multiple variables, you use multiple statements:
double weight = 60.5;
double height = 1.72;If variables have the same type, you can declare them in one statement and use a comma (,) to separate two variables like this:
double weight = 61.5,
height = 2.72;
Console.WriteLine($"The weight is {weight}kg and height is {height}m");Output:
The weight is 61.5kg and height is 1.72mC# Multiple and Multi-Line Variables Declaration
In c#, we can declare and initialize multiple variables of the same data type in a single line by separating with a comma(,).
Following is the example of defining the multiple variables of the same data type in a single line by separating with a comma(,) in the c# programming language:
int a, b, c;
float x, y, z = 1.5;While declaring the multiple variables of the same data type, we can arrange them in multiple lines to make them more readable. The compiler will treat it as a single statement until it encounters a semicolon (;).
Following is the simple of defining the multiple variables of the same data type in multiple lines in c# programming language.
int a,
b,
c;
float x,y,
z = 1.5;C# Display variables
To output the age variable to the console, you use the Console.WriteLine method as follows:
int age = 22;
Console.WriteLine(age);Output:
22To embed the age variable in a string and display it, you use the following statement:
int age = 22;
Console.WriteLine($"The age is {age}");Output:
The age is 22;In this statement:
- First, prefix the string with the
$symbol. - Second, place the variable (
age) inside the curly braces{}.
When the compiler sees a string with the $ prefix, it’ll replace all the variables in the curly braces with their corresponding values.
Definite Assignment (C# Variables Assignment)
- C# enforces a definite assignment policy.
- Local variables must be assigned to a value before using.
- Method arguments must be supplied when a method is called.
- All other variables are initialized by the runtime.
- Fields and array elements are automatically initialized to default values for their type.
The following code outputs 0, since array elements are implicitly assigned to their default values:
static void Main() {
int[] ints = new int[2];
Console.WriteLine (ints[0]); // 0
} The following code outputs 0, because fields are implicitly assigned a default value:
class Test {
static int x;
static void Main() {
Console.WriteLine (x);
}
}The code above generates the following result:
0In c#, once we declare and assign a value to the variable that can be assigned to another variable of the same data type.
Following is the example of assigning a value of one variable to another variable of the same type in c# programming language:
int a = 522;
int b = a;
string name = "test";
string firstname = name;In c#, it’s mandatory to assign a value to the variable before we use it; otherwise, we will get a compile-time error.
If we try to assign a value of string data type to an integer data type or vice versa, as shown below, we will get an error like “cannot implicitly convert type int to string”.
int b = 500;
string name = b;Default Values
- All type instances have a default value.
The following table lists the the default value for the predefined types:
| Type | Default value |
|---|---|
All reference types | null |
All numeric and enum types | 0 |
char type | '\0' |
bool type | false |
We can get the default value for any type using the default keyword:
decimal d = default (decimal);The default value in a custom value type, for example struct, is the same as the default value for each field.
C# variable example
The following example uses various types of variables:
using System;
namespace VariableDefinition
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
short a;
int b ;
double c;
/* actual initialization */
a = 10;
b = 20;
c = a + b;
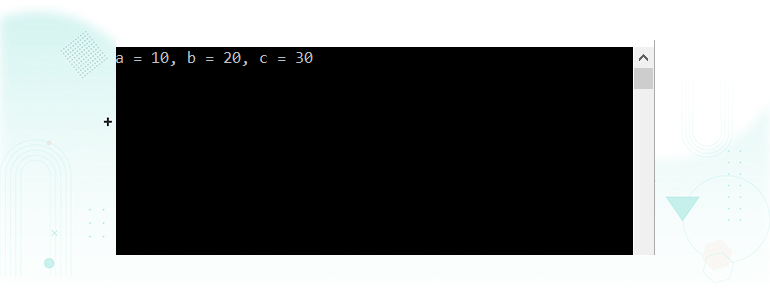
Console.WriteLine("a = {0}, b = {1}, c = {2}", a, b, c);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
Accepting Values from User
The Console class in the System namespace provides a function ReadLine() for accepting input from the user and store it into a variable.
For example:
int num;
num = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine());The function Convert.ToInt32() converts the data entered by the user to int data type, because Console.ReadLine() accepts the data in string format.
Lvalue and Rvalue Expressions in C#
There are two kinds of expressions in C#:
lvalue: An expression that is an lvalue may appear as either the left-hand or right-hand side of an assignment.rvalue: An expression that is an rvalue may appear on the right- but not left-hand side of an assignment.
Rules for defining variables
- A variable can have alphabets, digits and underscore.
- A variable name can start with alphabet and underscore only. It can't start with digit.
- No white space is allowed within variable name.
- A variable name must not be any reserved word or keyword e.g. char, float etc.
The following are some valid ways to define the variable names in the c# programming language:
int x;
string _y;
int m20;
float a2b;
char _abc;The following are some of the Invalid ways of defining the variable names in the c# programming language:
int 5;
int x y;
int double;
float 2abc;
char &abc;
double int;Related Tutorials:
- C# Data Types
- C# Types of Variables
- C# Integer Variable Types
- C# Floating Point Variables
- C# Boolean Variable Type
- C# Character Variable Type
- C# String Variables
- C# Casting Variable Types
- C# Implicitly Typed Local Variable: C# Var keyword
- C# Keywords
- C# Comments
- C# Parameters
- C# Constants
- C# Value and Reference Types
- C# Numeric Types
- C# Numeric Value
- C# User Input